Automated Software Testing Series - Visual Studio Toolbox
12 videos
Welcome to the 12-part series on automated software testing, where you will learn how to increase the efficiency and ROI of your software testing. We cover unit testing, behavior style testing, mocking, integration testing and more.
ثبت نام در Modern Workplace
ساخت یک Microservice با NET 5.
This video shows how to create a microservice from scratch using .NET 5. You will learn:
• How to create a .NET 5 microservice from scratch
• Build and debug a .NET 5 project in VS Code
• Interact with your microservice endpoints via Open API and Postman
• Keep configuration and secrets separate from your service code
• Simplify http requests to external endpoints
• Deal with transient errors on external services
• Report the health of the service and its dependencies
• Produce logs suited for a microservice environment
Request URL: http://localhost:5000/api/office?page=1&pageSize=5
Request Method: GET Status Code: 401 Unauthorized Remote Address: [::1]:5000 Referrer Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Security;
namespace OpenIDExample.Models
{
#region Models
public class ChangePasswordModel
{
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Current password")]
public string OldPassword { get; set; }
[Required]
[ValidatePasswordLength]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "New password")]
public string NewPassword { get; set; }
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Confirm new password")]
[Compare("NewPassword", ErrorMessage = "The new password and confirmation password do not match.")]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; }
}
public class LogOnModel
{
[Display(Name = "OpenID")]
public string OpenID { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name = "User name")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Password")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Remember me?")]
public bool RememberMe { get; set; }
}
public class RegisterModel
{
[Display(Name = "OpenID")]
public string OpenID { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name = "User name")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.EmailAddress)]
[Display(Name = "Email address")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
[ValidatePasswordLength]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Password")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Confirm password")]
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "The password and confirmation password do not match.")]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; }
}
#endregion Models
#region Services
// The FormsAuthentication type is sealed and contains static members, so it is difficult to
// unit test code that calls its members. The interface and helper class below demonstrate
// how to create an abstract wrapper around such a type in order to make the AccountController
// code unit testable.
public interface IMembershipService
{
int MinPasswordLength { get; }
bool ValidateUser(string userName, string password);
MembershipCreateStatus CreateUser(string userName, string password, string email, string OpenID);
bool ChangePassword(string userName, string oldPassword, string newPassword);
MembershipUser GetUser(string OpenID);
}
public class AccountMembershipService : IMembershipService
{
private readonly MembershipProvider _provider;
public AccountMembershipService()
: this(null)
{
}
public AccountMembershipService(MembershipProvider provider)
{
_provider = provider ?? Membership.Provider;
}
public int MinPasswordLength
{
get
{
return _provider.MinRequiredPasswordLength;
}
}
public bool ValidateUser(string userName, string password)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(userName)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "userName");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(password)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "password");
return _provider.ValidateUser(userName, password);
}
public Guid StringToGUID(string value)
{
// Create a new instance of the MD5CryptoServiceProvider object.
MD5 md5Hasher = MD5.Create();
// Convert the input string to a byte array and compute the hash.
byte[] data = md5Hasher.ComputeHash(Encoding.Default.GetBytes(value));
return new Guid(data);
}
public MembershipCreateStatus CreateUser(string userName, string password, string email, string OpenID)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(userName)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "userName");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(password)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "password");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(email)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "email");
MembershipCreateStatus status;
_provider.CreateUser(userName, password, email, null, null, true, StringToGUID(OpenID), out status);
return status;
}
public MembershipUser GetUser(string OpenID)
{
return _provider.GetUser(StringToGUID(OpenID), true);
}
public bool ChangePassword(string userName, string oldPassword, string newPassword)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(userName)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "userName");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(oldPassword)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "oldPassword");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(newPassword)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "newPassword");
// The underlying ChangePassword() will throw an exception rather
// than return false in certain failure scenarios.
try
{
MembershipUser currentUser = _provider.GetUser(userName, true /* userIsOnline */);
return currentUser.ChangePassword(oldPassword, newPassword);
}
catch (ArgumentException)
{
return false;
}
catch (MembershipPasswordException)
{
return false;
}
}
public MembershipCreateStatus CreateUser(string userName, string password, string email)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
public interface IFormsAuthenticationService
{
void SignIn(string userName, bool createPersistentCookie);
void SignOut();
}
public class FormsAuthenticationService : IFormsAuthenticationService
{
public void SignIn(string userName, bool createPersistentCookie)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(userName)) throw new ArgumentException("Value cannot be null or empty.", "userName");
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(userName, createPersistentCookie);
}
public void SignOut()
{
FormsAuthentication.SignOut();
}
}
#endregion Services
#region Validation
public static class AccountValidation
{
public static string ErrorCodeToString(MembershipCreateStatus createStatus)
{
// See http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=177550 for
// a full list of status codes.
switch (createStatus)
{
case MembershipCreateStatus.DuplicateUserName:
return "Username already exists. Please enter a different user name.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.DuplicateEmail:
return "A username for that e-mail address already exists. Please enter a different e-mail address.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword:
return "The password provided is invalid. Please enter a valid password value.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidEmail:
return "The e-mail address provided is invalid. Please check the value and try again.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidAnswer:
return "The password retrieval answer provided is invalid. Please check the value and try again.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidQuestion:
return "The password retrieval question provided is invalid. Please check the value and try again.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidUserName:
return "The user name provided is invalid. Please check the value and try again.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.ProviderError:
return "The authentication provider returned an error. Please verify your entry and try again. If the problem persists, please contact your system administrator.";
case MembershipCreateStatus.UserRejected:
return "The user creation request has been canceled. Please verify your entry and try again. If the problem persists, please contact your system administrator.";
default:
return "An unknown error occurred. Please verify your entry and try again. If the problem persists, please contact your system administrator.";
}
}
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = true)]
public sealed class ValidatePasswordLengthAttribute : ValidationAttribute, IClientValidatable
{
private const string _defaultErrorMessage = "'{0}' must be at least {1} characters long.";
private readonly int _minCharacters = Membership.Provider.MinRequiredPasswordLength;
public ValidatePasswordLengthAttribute()
: base(_defaultErrorMessage)
{
}
public override string FormatErrorMessage(string name)
{
return String.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, ErrorMessageString,
name, _minCharacters);
}
public override bool IsValid(object value)
{
string valueAsString = value as string;
return (valueAsString != null && valueAsString.Length >= _minCharacters);
}
public IEnumerable<ModelClientValidationRule> GetClientValidationRules(ModelMetadata metadata, ControllerContext context)
{
return new[]{
new ModelClientValidationStringLengthRule(FormatErrorMessage(metadata.GetDisplayName()), _minCharacters, int.MaxValue)
};
}
}
#endregion Validation
}
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Routing;
using System.Web.Security;
using DotNetOpenAuth.Messaging;
using DotNetOpenAuth.OpenId;
using DotNetOpenAuth.OpenId.RelyingParty;
using OpenIDExample.Models;
namespace OpenIDExample.Controllers
{
public class AccountController : Controller
{
private static OpenIdRelyingParty openid = new OpenIdRelyingParty();
public IFormsAuthenticationService FormsService { get; set; }
public IMembershipService MembershipService { get; set; }
protected override void Initialize(RequestContext requestContext)
{
if (FormsService == null) { FormsService = new FormsAuthenticationService(); }
if (MembershipService == null) { MembershipService = new AccountMembershipService(); }
base.Initialize(requestContext);
}
// **************************************
// URL: /Account/LogOn
// **************************************
public ActionResult LogOn()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult LogOn(LogOnModel model, string returnUrl)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
if (MembershipService.ValidateUser(model.UserName, model.Password))
{
FormsService.SignIn(model.UserName, model.RememberMe);
if (Url.IsLocalUrl(returnUrl))
{
return Redirect(returnUrl);
}
else
{
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "The user name or password provided is incorrect.");
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
return View(model);
}
// **************************************
// URL: /Account/LogOff
// **************************************
public ActionResult LogOff()
{
FormsService.SignOut();
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
// **************************************
// URL: /Account/Register
// **************************************
public ActionResult Register(string OpenID)
{
ViewBag.PasswordLength = MembershipService.MinPasswordLength;
ViewBag.OpenID = OpenID;
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Register(RegisterModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
// Attempt to register the user
MembershipCreateStatus createStatus = MembershipService.CreateUser(model.UserName, model.Password, model.Email, model.OpenID);
if (createStatus == MembershipCreateStatus.Success)
{
FormsService.SignIn(model.UserName, false /* createPersistentCookie */);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", AccountValidation.ErrorCodeToString(createStatus));
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
ViewBag.PasswordLength = MembershipService.MinPasswordLength;
return View(model);
}
// **************************************
// URL: /Account/ChangePassword
// **************************************
[Authorize]
public ActionResult ChangePassword()
{
ViewBag.PasswordLength = MembershipService.MinPasswordLength;
return View();
}
[Authorize]
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult ChangePassword(ChangePasswordModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
if (MembershipService.ChangePassword(User.Identity.Name, model.OldPassword, model.NewPassword))
{
return RedirectToAction("ChangePasswordSuccess");
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "The current password is incorrect or the new password is invalid.");
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
ViewBag.PasswordLength = MembershipService.MinPasswordLength;
return View(model);
}
// **************************************
// URL: /Account/ChangePasswordSuccess
// **************************************
public ActionResult ChangePasswordSuccess()
{
return View();
}
[ValidateInput(false)]
public ActionResult Authenticate(string returnUrl)
{
var response = openid.GetResponse();
if (response == null)
{
//Let us submit the request to OpenID provider
Identifier id;
if (Identifier.TryParse(Request.Form["openid_identifier"], out id))
{
try
{
var request = openid.CreateRequest(Request.Form["openid_identifier"]);
return request.RedirectingResponse.AsActionResult();
}
catch (ProtocolException ex)
{
ViewBag.Message = ex.Message;
return View("LogOn");
}
}
ViewBag.Message = "Invalid identifier";
return View("LogOn");
}
//Let us check the response
switch (response.Status)
{
case AuthenticationStatus.Authenticated:
LogOnModel lm = new LogOnModel();
lm.OpenID = response.ClaimedIdentifier;
//check if user exist
MembershipUser user = MembershipService.GetUser(lm.OpenID);
if (user != null)
{
lm.UserName = user.UserName;
FormsService.SignIn(user.UserName, false);
}
return View("LogOn", lm);
case AuthenticationStatus.Canceled:
ViewBag.Message = "Canceled at provider";
return View("LogOn");
case AuthenticationStatus.Failed:
ViewBag.Message = response.Exception.Message;
return View("LogOn");
}
return new EmptyResult();
}
}
}
6- سپس برای Action به نام LogOn یک View میسازیم، برای Authenticate نیازی به ایجاد View ندارد چون قرار است درخواست کاربر را به آدرس دیگری Redirect کند. سپس کدهای زیر را برای View ایجاد شده وارد میکنیم.
@model OpenIDExample.Models.LogOnModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Log On";
}
<h2>
Log On</h2>
<p>
Please enter your username and password. @Html.ActionLink("Register", "Register")
if you don't have an account.
</p>
<script src="@Url.Content("~/Scripts/jquery.validate.min.js")" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="@Url.Content("~/Scripts/jquery.validate.unobtrusive.min.js")" type="text/javascript"></script>
<form action="Authenticate?ReturnUrl=@HttpUtility.UrlEncode(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"])" method="post" id="openid_form">
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="verify" />
<div>
<fieldset>
<legend>Login using OpenID</legend>
<div class="openid_choice">
<p>
Please click your account provider:</p>
<div id="openid_btns">
</div>
</div>
<div id="openid_input_area">
@Html.TextBox("openid_identifier")
<input type="submit" value="Log On" />
</div>
<noscript>
<p>
OpenID is service that allows you to log-on to many different websites using a single
indentity. Find out <a href="http://openid.net/what/">more about OpenID</a> and
<a href="http://openid.net/get/">how to get an OpenID enabled account</a>.</p>
</noscript>
<div>
@if (Model != null)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(Model.UserName))
{
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.OpenID)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.OpenID)
</div>
<p class="button">
@Html.ActionLink("New User ,Register", "Register", new { OpenID = Model.OpenID })
</p>
}
else
{
//user exist
<p class="buttonGreen">
<a href="@Url.Action("Index", "Home")">Welcome , @Model.UserName, Continue..." </a>
</p>
}
}
</div>
</fieldset>
</div>
</form>
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "Login was unsuccessful. Please correct the errors and try again.")
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
<div>
<fieldset>
<legend>Or Login Normally</legend>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.UserName)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.UserName)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.UserName)
</div>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Password)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Password)
</div>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.CheckBoxFor(m => m.RememberMe)
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.RememberMe)
</div>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Log On" />
</p>
</fieldset>
</div>
}
پس از اجرای پروژه صفحه ای شبیه به پایین مشاهده کرده و سرویس دهنده OpenID خاص خود را میتوانید انتخاب نمایید.
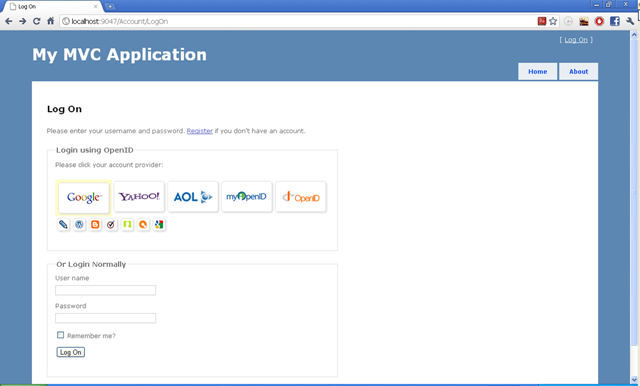
7- برای فعال سازی عملیات احراز هویت توسط FormsAuthentication در سایت باید تنطیمات زیر را در فایل web.config انجام دهید.
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms loginUrl="~/Account/LogOn" timeout="2880" />
</authentication>
جهت مطالعات بیشتر ودانلود نمونه کدهای آماده میتوانید به لینکهای (^ و ^ و ^ و ^ و ^ و ^ و ^ ) مراجعه کنید.
کد کامل پروژه را میتوانید از اینجا دانلود نمایید.
منبع
کلیدهای مربوط به Request
| ضروری؟ | نام کلید | مقدار |
| بله | "owin.RequestBody" | یک Stream همراه با request body. اگر body برای request وجود نداشته باشد، Stream.Null به عنوان placeholder قابل استفاده است. |
| بله | "owin.RequestHeaders" | یک دیکشنری به صورت IDictionary<string, string[]> از هدرهای درخواست. |
| بله | "owin.RequestMethod" | رشتهایی حاوی نوع فعل متد HTTP مربوط به درخواست (مانند GET and POST ) |
| بله | "owin.RequestPath" | path درخواست شده به صورت string |
| بله | "owin.RequestPathBase" | قسمتی از path درخواست به صورت string |
| بله | "owin.RequestProtocol" | نام و نسخهی پروتکل (مانند HTTP/1.0 or HTTP/1.1 ) |
| بله | "owin.RequestQueryString" | رشتهای حاوی query string ؛ بدون علامت ? (مانند foo=bar&baz=quux ) |
| بله | "owin.RequestScheme" | رشتهایی حاوی URL scheme استفاده شده در درخواست (مانند HTTP or HTTPS ) |
| ضروری؟ | نام کلید | مقدار |
| بله | "owin.ResponseBody" | یک Stream جهت نوشتن response body در خروجی |
| بله | "owin.ResponseHeaders" | یک دیکشنری به صورت IDictionary<string, string[]> از هدرهای response |
| خیر | "owin.ResponseStatusCode" | یک عدد صحیح حاوی کد وضعیت HTTP response ؛ حالت پیشفرض 200 است. |
| خیر | "owin.ResponseReasonPhrase" | یک رشته حاوی reason phrase مربوط به status code ؛ اگر خالی باشد در نتیجه سرور بهتر است آن را مقداردهی کند. |
| خیر | "owin.ResponseProtocol" | یک رشته حاوی نام و نسخهی پروتکل (مانند HTTP/1.0 or HTTP/1.1 )؛ اگر خالی باشد؛ “owin.RequestProtocol” به عنوان مقدار پیشفرض در نظر گرفته خواهد شد. |
<package id="Microsoft.Owin" version="3.0.1" targetFramework="net461" /> <package id="Microsoft.Owin.Host.SystemWeb" version="3.0.1" targetFramework="net461" /> <package id="Owin" version="1.0" targetFramework="net461" />
using Owin;
namespace SimpleOwinWebApp
{
public class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
}
}
} using Owin;
namespace SimpleOwinWebApp
{
public class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
app.Use(async (ctx, next) =>
{
await ctx.Response.WriteAsync("Hello");
});
}
} Func<IOwinContext, Func<Task>, Task> handler
app.Use(async (ctx, next) =>
{
var response = ctx.Environment["owin.ResponseBody"] as Stream;
using (var writer = new StreamWriter(response))
{
await writer.WriteAsync("Hello");
}
}); 
using System;
using Microsoft.Owin.Hosting;
namespace SimpleOwinConsoleApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (WebApp.Start<Startup>("http://localhost:12345"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Listening to port 12345");
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to end...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
} using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace SimpleOwinCoreApp
{
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
loggerFactory.AddConsole();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
}
}
} using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
namespace SimpleOwinCoreApp.Middlewares
{
public class SimpleMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public SimpleMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext ctx)
{
// قبل از فراخوانی میانافزار بعدی
await ctx.Response.WriteAsync("Hello DNT!");
await _next(ctx);
// بعد از فراخوانی میانافزار بعدی
}
}
} app.UseMiddleware<SimpleMiddleware>();
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Owin": "1.0.0"
app.UseOwin(pipeline =>
{
pipeline(next => new MyKatanaBasedMiddleware(next).Invoke)
}); using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
namespace SimpleOwinAspNetCore.Middleware
{
public class IpBlockerMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly IpBlockerOptions _options;
public IpBlockerMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IpBlockerOptions options)
{
_next = next;
_options = options;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
var ipAddress = context.Request.Host.Host;
if (IsBlockedIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 403;
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Forbidden : The server understood the request, but It is refusing to fulfill it.");
return;
}
await _next.Invoke(context);
}
private bool IsBlockedIpAddress(string ipAddress)
{
return _options.Ips.Any(ip => ip == ipAddress);
}
}
} using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SimpleOwinAspNetCore.Middleware
{
public class IpBlockerOptions
{
public IpBlockerOptions()
{
Ips = new[] { "192.168.1.1" };
}
public IList<string> Ips { get; set; }
}
} using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
namespace SimpleOwinAspNetCore.Middleware
{
public static class IpBlockerExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseIpBlocker(this IApplicationBuilder builder, IConfigurationRoot configuration, IpBlockerOptions options = null)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<IpBlockerMiddleware>(options ?? new IpBlockerOptions
{
Ips = configuration.GetSection("block_list").GetChildren().Select(p => p.Value).ToArray()
});
}
}
} {
"block_list": [
"192.168.1.1",
"localhost",
"127.0.0.1",
"172.16.132.151"
]
} public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { set; get; }
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("blockedIps.json");
Configuration = builder.Build();
} app.UseIpBlocker(Configuration);
Disabling GitHub Discussions tab for dotnet/aspnetcore






